ABOUT THE PROTOCOL
CHAdeMO is a DC charging protocol currently enabling EV charging with power from 6kW to 400kW with 900kW in preparation. It follows 4 principles:

SAFETY
CHAdeMO mandates strict guidelines in designing chargers to guarantee electrical safety in any operating conditions.

FUTURE-PROOF
CHAdeMO is Smart Grid-ready through its bi-directional charging capability. It is also compatible with any local or optional functions beyond charging.

EASE OF APPLICATION
The protocol works with CAN communication, onboard communication network for all EVs, making its integration with the rest of the car easy and reliable.
UNIFORMITY
CHAdeMO connector is identical across the globe and is a stand-alone plug that can be with or without an AC connector. It saves costs for EV makers and enables cross-continental EV travels.
TECHNICAL DETAILS
Battery protection
The current is controlled by the vehicle ECU. Fast charger controls the output current according to the charging current request from the EV through CAN communication on a real-time basis. This mechanism allows for different fast charging based on battery performance and usage environment. To do so, CHAdeMO specifies the requirements for response performance, current ripple, voltage ripple, and measurement accuracy of the current and voltage.
Protection from electrical shock
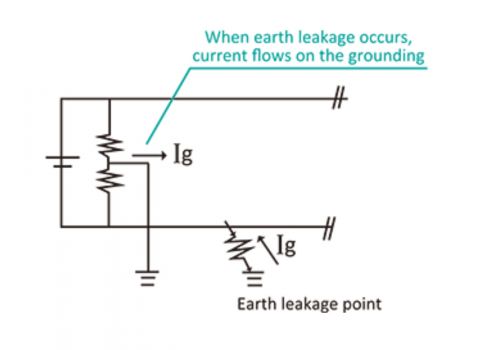
- The isolation transformer inside the charger separates the AC system at the input side and the DC system at the output side, therefore, the output side is a non-earthed system and the electric shock can be avoided if an earth leakage fault occurs on one of the DC lines.
- A leakage current monitoring device is installed at the DC side as well as the AC side and it shuts down input power to the charger as soon as leakage current is detected. The electrical shock protection in the DC-2 zone stipulated under IEC60479-1 was realized by combining the leakage current monitoring and immediate automatic disconnection.
Fail-safe of charging control
- In some cases, a malfunction may occur during charging at the vehicle and charger monitor level. Two communication lines (CAN signal and Pilot signal) from the vehicle to the charger are in place to send a signal in case a malfunction is detected on the vehicle side. This way, charging will stop even if one communication line is broken.
- When the vehicle coupler is dropped, the disconnection of the grounding wire and the pilot wire causes each Pilot signal to turn OFF, which puts a halt to the DC output immediately, so that the electrical arcing stops.
Interlock of connector
- Given that the control power is supplied to EV contactors via a charger, EV contactors never close and there is zero voltage unless a vehicle coupler is connected to the vehicle.
- Pre-charge Automatic Safety Check is a test conducted before each charge to check the circuit insulation and the short circuit between the charger and EV contactors.
- During charging, the vehicle coupler is locked to the vehicle inlet via a mechanical latch, and the mechanical latch is locked by a electrical lock. Once charging is completed, the electric lock is released after confirming the voltage on a vehicle connector. If the voltage does not drop to a safety level, the lock will not be released.